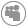
+ ou - 7 mm
Mais j'ai de l'ambition.
Retourner vers Je débute en Hi-Fi
+ ou - 7 mm
![]() #1 par Nicodimdom » 22 Mar 2017 à 14:20
#1 par Nicodimdom » 22 Mar 2017 à 14:20
J'ai un doute !  Question idiote peut-être mais que faut-il entendre quand on lit à propos d'un HP que le déplacement de la membrane (possible sans problème j'imagine) est de + / - 7 mm ?
Question idiote peut-être mais que faut-il entendre quand on lit à propos d'un HP que le déplacement de la membrane (possible sans problème j'imagine) est de + / - 7 mm ?
Cela signifie-t-il que
1/ par rapport au plan délimité par la membrane lorsqu'elle est immobile, le HP en action peut avancer de 7 mm ET reculer de 7 mm aussi soit un déplacement admissible total de +7 / - 7 = 14 mm entre la position de recul maximum et la position d' avance maximum
ou
2/ la distance de déplacement total de la membrane est de 7 mm environ au total (soit 3,5 de recul maxi de la membrane et 3,5 d'avance maxi). ?
Merci.
Cela signifie-t-il que
1/ par rapport au plan délimité par la membrane lorsqu'elle est immobile, le HP en action peut avancer de 7 mm ET reculer de 7 mm aussi soit un déplacement admissible total de +7 / - 7 = 14 mm entre la position de recul maximum et la position d' avance maximum
ou
2/ la distance de déplacement total de la membrane est de 7 mm environ au total (soit 3,5 de recul maxi de la membrane et 3,5 d'avance maxi). ?
Merci.
Dom
LES ENCEINTES FRANCAISES, c'est LE PIED !! (Pas un pied d'argile comme les enceintes en glaise)
LES ENCEINTES FRANCAISES, c'est LE PIED !! (Pas un pied d'argile comme les enceintes en glaise)
-

Nicodimdom - 500 watts

- Messages: 7130
- Inscription: 21 Oct 2012 à 23:31
- Localisation: Puy-L'Evêque (LOT)
-
Re: + ou - 7 mm
![]() #2 par PFB » 22 Mar 2017 à 14:37
#2 par PFB » 22 Mar 2017 à 14:37
Salut,
De toute façon une indication technique sans donner de cadre ne vaut pas un sous.
Alors que ce soit 14mm, +/-7mm, 3,5mm à gauche et le reste à droite, ça ne vaut rien.
14mm avant destruction, alors on commence à percevoir une indication,
14mm à 1000Hz c'est sûr que j'entend qqch.
ou 14mm à 1% de distortion, là c'est l'épate...
PFB
De toute façon une indication technique sans donner de cadre ne vaut pas un sous.
Alors que ce soit 14mm, +/-7mm, 3,5mm à gauche et le reste à droite, ça ne vaut rien.
14mm avant destruction, alors on commence à percevoir une indication,
14mm à 1000Hz c'est sûr que j'entend qqch.
ou 14mm à 1% de distortion, là c'est l'épate...
PFB
20 ans de progression entropique
-

PFB - 100 watts

- Messages: 2299
- Inscription: 22 Jan 2016 à 11:15
- Localisation: Pays de Vaud, terres septentrionales de Savoie
Re: + ou - 7 mm
![]() #3 par peyrerouge » 22 Mar 2017 à 14:42
#3 par peyrerouge » 22 Mar 2017 à 14:42
Nicodimdom part en excursion...
"...No dark sarcasm in the classroom..."
UNE MERVEILLE: LOVE I OBEY https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=is3ilPcIwFA
OUVERTURE Mozart: birthday https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qg8q1VjjeWo
UNE MERVEILLE: LOVE I OBEY https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=is3ilPcIwFA
OUVERTURE Mozart: birthday https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qg8q1VjjeWo
-

peyrerouge - 500 watts

- Messages: 6935
- Inscription: 21 Oct 2010 à 18:08
- Localisation: Ariège Pyrénées
-
Re: + ou - 7 mm
![]() #4 par bricoleur » 22 Mar 2017 à 14:45
#4 par bricoleur » 22 Mar 2017 à 14:45
https://www.eminence.com/support/unders ... aker-data/
XMAX/XLIM
Short for Maximum Linear Excursion. Speaker output becomes non-linear when the voice coil begins to leave the magnetic gap. Although suspensions can create non-linearity in output, the point at which the number of turns in the gap (see BL) begins to decrease is when distortion starts to increase. Eminence has historically been very conservative with this measurement and indicated only the voice coil overhang (Xmax: Voice coil height minus top plate thickness, divided by 2). The Xmax figures on this website are expressed as the greater of the result of the formula above or the excursion point of the woofer where THD reahes 10%. This method results in a more real world expression of the usable excursion limit for the transducer. Xlim is expressed by Eminence as the lowest of four potential failure condition measurements: spider crashing on top plate; Voice coil bottoming on back plate; Voice coil coming out of gap above core; or the physical limitation of cone. A transducer exceeding the Xlim is certain to fail from one of these conditions. High pass filters, limiters, and enclosure modeling software programs are valuable tools in protecting your woofers from mechanical failure.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thiele/Small
Large signal parameters[edit]
These parameters are useful for predicting the approximate output of a driver at high input levels, though they are harder, sometimes extremely hard or impossible, to accurately measure. In addition, power compression, thermal, and mechanical effects due to high signal levels (e.g., high electric current and voltage, extended mechanical motion, and so on) all change driver behavior, often increasing distortion of several kinds.
Xmax - Maximum linear peak (or sometimes peak-to-peak) excursion (in mm) of the cone. Note that, because of mechanical issues, the motion of a driver cone becomes non-linear with large excursions, especially those in excess of this parameter.
Xmech - Maximum physical excursion of the driver before physical damage. With a sufficiently large electrical input, the excursion will cause damage to the voice coil or another moving part of the driver. In addition, arrangements for voice coil cooling (e.g., venting of the pole piece, or openings in the voice coil former above the coil itself, both allowing heat dissipation with air flow) will themselves change behaviors with large cone excursions.
Pe - Thermal power handling capacity of the driver, in watts. This value is difficult to characterize and is often overestimated, by manufacturers and others. As the voice coil heats, it changes dimension to some extent, and changes electrical resistance to a considerable extent. The latter changes the electrical relationships between the voice coil and passive crossover components, changing the slope and crossover points designed into the speaker system.
Vd - Peak displacement volume, calculated by Vd = Sd·Xmax
XMAX/XLIM
Short for Maximum Linear Excursion. Speaker output becomes non-linear when the voice coil begins to leave the magnetic gap. Although suspensions can create non-linearity in output, the point at which the number of turns in the gap (see BL) begins to decrease is when distortion starts to increase. Eminence has historically been very conservative with this measurement and indicated only the voice coil overhang (Xmax: Voice coil height minus top plate thickness, divided by 2). The Xmax figures on this website are expressed as the greater of the result of the formula above or the excursion point of the woofer where THD reahes 10%. This method results in a more real world expression of the usable excursion limit for the transducer. Xlim is expressed by Eminence as the lowest of four potential failure condition measurements: spider crashing on top plate; Voice coil bottoming on back plate; Voice coil coming out of gap above core; or the physical limitation of cone. A transducer exceeding the Xlim is certain to fail from one of these conditions. High pass filters, limiters, and enclosure modeling software programs are valuable tools in protecting your woofers from mechanical failure.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thiele/Small
Large signal parameters[edit]
These parameters are useful for predicting the approximate output of a driver at high input levels, though they are harder, sometimes extremely hard or impossible, to accurately measure. In addition, power compression, thermal, and mechanical effects due to high signal levels (e.g., high electric current and voltage, extended mechanical motion, and so on) all change driver behavior, often increasing distortion of several kinds.
Xmax - Maximum linear peak (or sometimes peak-to-peak) excursion (in mm) of the cone. Note that, because of mechanical issues, the motion of a driver cone becomes non-linear with large excursions, especially those in excess of this parameter.
Xmech - Maximum physical excursion of the driver before physical damage. With a sufficiently large electrical input, the excursion will cause damage to the voice coil or another moving part of the driver. In addition, arrangements for voice coil cooling (e.g., venting of the pole piece, or openings in the voice coil former above the coil itself, both allowing heat dissipation with air flow) will themselves change behaviors with large cone excursions.
Pe - Thermal power handling capacity of the driver, in watts. This value is difficult to characterize and is often overestimated, by manufacturers and others. As the voice coil heats, it changes dimension to some extent, and changes electrical resistance to a considerable extent. The latter changes the electrical relationships between the voice coil and passive crossover components, changing the slope and crossover points designed into the speaker system.
Vd - Peak displacement volume, calculated by Vd = Sd·Xmax
-

bricoleur - 50 watts

- Messages: 652
- Inscription: 24 Oct 2010 à 14:39
- Localisation: Sud Oise
Re: + ou - 7 mm
![]() #5 par Nicodimdom » 22 Mar 2017 à 14:52
#5 par Nicodimdom » 22 Mar 2017 à 14:52
PFB a écrit:Salut,
De toute façon une indication technique sans donner de cadre ne vaut pas un sous.
Alors que ce soit 14mm, +/-7mm, 3,5mm à gauche et le reste à droite, ça ne vaut rien.
14mm avant destruction, alors on commence à percevoir une indication,
14mm à 1000Hz c'est sûr que j'entend qqch.
ou 14mm à 1% de distortion, là c'est l'épate...
PFB
OK. OK. Tu interprètes. On est d'accord sur le fond mais pour que je t'excurse (ça c'est pour Peyrerouge) de répondre ainsi, réponds à la question que je pose qui est celle de la forme:
Quand tu dis: 14mm avant destruction, alors on commence à percevoir une indication,
14mm à 1000Hz c'est sûr que j'entend qqch.
ou 14mm à 1% de distortion, là c'est l'épate...
c'est traditionnellement dans la langue courante des fabricants 14mm (déplacement avant) + 14 mm (déplacement arrière) ou environ 14 mm au total (c. à. d. 7 avant et 7 derrière ?
Dom
LES ENCEINTES FRANCAISES, c'est LE PIED !! (Pas un pied d'argile comme les enceintes en glaise)
LES ENCEINTES FRANCAISES, c'est LE PIED !! (Pas un pied d'argile comme les enceintes en glaise)
-

Nicodimdom - 500 watts

- Messages: 7130
- Inscription: 21 Oct 2012 à 23:31
- Localisation: Puy-L'Evêque (LOT)
-
Re: + ou - 7 mm
![]() #6 par dsdn » 22 Mar 2017 à 15:00
#6 par dsdn » 22 Mar 2017 à 15:00
Bonjour
C'est une convention industriel.
Une cote à + ou - 7mm, veut dire que la cote nominale peut être majorée ou minorée de 7mm. Ca fait donc 14 mm au total..
Si la tolérance avait été de +2mm, et -12 mm, c'aurait été spécifié.
DAvid
C'est une convention industriel.
Une cote à + ou - 7mm, veut dire que la cote nominale peut être majorée ou minorée de 7mm. Ca fait donc 14 mm au total..
Si la tolérance avait été de +2mm, et -12 mm, c'aurait été spécifié.
DAvid
-

dsdn - 100 watts

- Messages: 1491
- Inscription: 01 Déc 2012 à 04:40
- Localisation: seiches sur le loir
Re: + ou - 7 mm
![]() #7 par PFB » 22 Mar 2017 à 15:12
#7 par PFB » 22 Mar 2017 à 15:12
Nicodimdom a écrit:c'est traditionnellement dans la langue courante des fabricants 14mm (déplacement avant) + 14 mm (déplacement arrière) ou environ 14 mm au total (c. à. d. 7 avant et 7 derrière ?
En excursion, je commence à me déglinguer vers 18km, ce qui correspond à +/-9km en référence au milieu du parcours, mais vu que je ne connais pas forcément le milieu du parcours, je préfère causer de 18km...
Généralement les premiers km sont agréables, les raideurs déboulent passé la moitié.
PFB
20 ans de progression entropique
-

PFB - 100 watts

- Messages: 2299
- Inscription: 22 Jan 2016 à 11:15
- Localisation: Pays de Vaud, terres septentrionales de Savoie
Re: + ou - 7 mm
![]() #8 par Nicodimdom » 22 Mar 2017 à 23:53
#8 par Nicodimdom » 22 Mar 2017 à 23:53
OK. Merci à vous.
Dom
LES ENCEINTES FRANCAISES, c'est LE PIED !! (Pas un pied d'argile comme les enceintes en glaise)
LES ENCEINTES FRANCAISES, c'est LE PIED !! (Pas un pied d'argile comme les enceintes en glaise)
-

Nicodimdom - 500 watts

- Messages: 7130
- Inscription: 21 Oct 2012 à 23:31
- Localisation: Puy-L'Evêque (LOT)
-
Re: + ou - 7 mm
![]() #9 par Phil » 23 Mar 2017 à 00:29
#9 par Phil » 23 Mar 2017 à 00:29
Nicodimdom » 22 Mar 2017, 13:52 a écrit:c'est traditionnellement dans la langue courante des fabricants 14mm (déplacement avant) + 14 mm (déplacement arrière) ou environ 14 mm au total (c. à. d. 7 avant et 7 derrière ?
David t'as répondu sur ce point.
Généralement les fabricants indiquent deux valeurs :
- X-Max qui correspond au déplacement maxi de la bobine dans l'entrefer sans perte de flux ou BL.
- X-Damage qui correspond à l'excursion mécanique maximum avant qu'il n'y ait de la casse.
Ce sont donc des critères dont il faut tenir compte en fonction du HP choisi pour une application donnée, spécifiquement des HP de grave/sub. Ces paramètres ne sont donc jamais indiqués pour des tweeters ou compressions 1", des petits HP medium, les fabricants indiquent une fréquence et une pente mini de coupure.
Philippe
-

Phil - 100 watts

- Messages: 1635
- Inscription: 22 Oct 2010 à 09:44
Re: + ou - 7 mm
![]() #10 par zeroundemi » 23 Mar 2017 à 09:45
#10 par zeroundemi » 23 Mar 2017 à 09:45
..........
Dernière édition par zeroundemi le 30 Avr 2017 à 11:39, édité 1 fois.
-

zeroundemi - 100 watts

- Messages: 2701
- Inscription: 25 Oct 2010 à 19:18
Re: + ou - 7 mm
![]() #11 par pecheur1958 » 23 Mar 2017 à 10:12
#11 par pecheur1958 » 23 Mar 2017 à 10:12
Avec tout ça personne ne parle du diamètre du HP 
-

pecheur1958 - 100 watts

- Messages: 4876
- Inscription: 22 Oct 2010 à 21:06
- Localisation: Chambéry Savoie
-
Re: + ou - 7 mm
![]() #12 par Nicodimdom » 23 Mar 2017 à 14:23
#12 par Nicodimdom » 23 Mar 2017 à 14:23
Je ne suis ni inquiet ni préoccupé, juste curieux de ce que je lis sur les spécifications du HP qui pour moi n'étaient pas claires. Merci encore de vos explications.
Dom
LES ENCEINTES FRANCAISES, c'est LE PIED !! (Pas un pied d'argile comme les enceintes en glaise)
LES ENCEINTES FRANCAISES, c'est LE PIED !! (Pas un pied d'argile comme les enceintes en glaise)
-

Nicodimdom - 500 watts

- Messages: 7130
- Inscription: 21 Oct 2012 à 23:31
- Localisation: Puy-L'Evêque (LOT)
-
Retourner vers Je débute en Hi-Fi
Qui est en ligne
Utilisateurs parcourant ce forum: Aucun utilisateur enregistré et 3 invités
Développé par phpBB® Forum Software © phpBB Group
 Faire un don
Faire un don